By Adeyemi Kelechi Modupe.
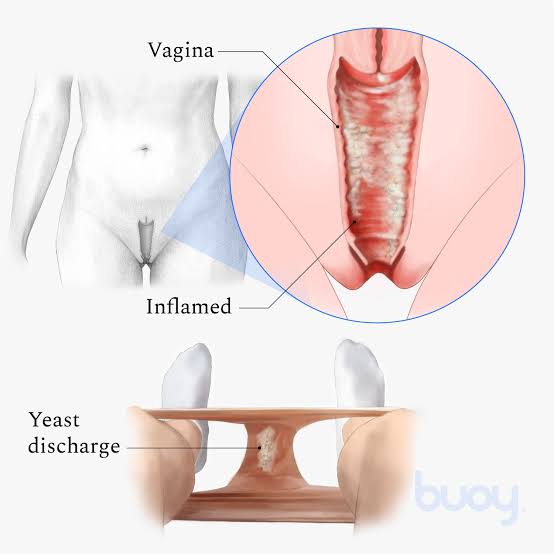
Yeast infections, caused by the Candida fungus, are a prevalent type of infection that can affect various parts of the body. The mouth, skin, and genitals, particularly the vagina, are common targets. Symptoms encompass itching, burning, discharge, and discomfort during sex. A combination of factors such as antibiotic use, diabetes, pregnancy, and weakened immune systems often contribute to their development.
When we think of yeast infections, the vaginal variety immediately comes to mind due to its common occurrence. Nevertheless, diverse forms of yeast infections exist, impacting different bodily regions. These include:
- Vaginal yeast infection (also termed vaginal candidiasis)
- Oral thrush (affecting the mouth and throat)
- Skin yeast infection (in warm, moist areas like the armpits, groin, and between toes)
- Candidemia (a severe systemic infection affecting the bloodstream)
- Invasive candidiasis (affecting internal organs like lungs, heart, or brain)
Our focus here is on invasive candidiasis, a serious condition where Candida fungus spreads from the bloodstream to internal organs. Though rare, it poses significant danger, primarily affecting individuals already suffering from serious illness or weakened immune systems.
Invasive candidiasis can be triggered by factors like prolonged antibiotic or steroid use, weakened immune systems due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or organ transplantation, extended hospital stays, mechanical ventilation, and chronic medical conditions like diabetes. The root cause often lies in a breakdown of the body’s natural defenses against infections. Although alarming, invasive candidiasis is fortunately infrequent.
The effects of invasive candidiasis can be daunting, encompassing fever, chills, confusion, organ failure (especially kidneys, liver, and lungs), bloodstream infections, skin infections, respiratory issues, and, in severe cases, shock and death.
Symptoms
Given its gravity, prompt medical intervention is essential. Its severity ranges from mild (localized infection, no symptoms) to moderate (fever, chills, flu-like symptoms) and severe (widespread infection, organ failure, death). The prognosis hinges on factors such as overall health, fungus type, and the timeliness of diagnosis and treatment.
Even successful treatment can leave lasting impacts, including scarring and organ damage, recurring infections (especially in immunocompromised individuals), infertility, increased risk of future infections, and chronic fatigue. Invasive candidiasis is a matter not to be taken lightly; its effects can persist long after the infection subsides.
Prevention remains the best strategy. Practicing good hygiene, minimizing antibiotic use, managing chronic conditions, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and practicing safe sex are crucial. A robust immune system bolstered by a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep also plays a pivotal role.
Treatment for Yeast Infections
Treatment often involves antifungal medications such as fluconazole or amphotericin B, with specifics tailored to infection location and severity. Surgical drainage or removal of infected tissue might be necessary. Severe cases require intensive care. Timely diagnosis and adherence to medical advice are imperative.
- You Are Gradually Destroying Your Brain When Doing These 5 Things
- How Much will it Cost to Install Solar Panels for Home in Nigeria
Invasive candidiasis spreads via the bloodstream, contaminated surfaces, person-to-person contact (rare in healthcare settings), and the digestive tract through contaminated food or medical procedures. Despite its transmission potential, it’s not as contagious as the flu or COVID-19, especially for individuals with robust immune systems.
Understanding yeast infections, particularly the invasive kind, underscores the need for awareness, prevention, and timely treatment. So, while it’s not a condition to be overly concerned about, vigilance and action are still key in managing its potential risks.
Adeyemi Kelechi Modupe,
Student of Mass Communication,
Prince Abubakar Audu University.